07.12.2023
What is the difference between a public, private, and hybrid cloud?
Share

Let's be clear right away. There is no "best" solution in the cloud. Every organization operates differently, and that calls for a different cloud environment; whether it's public, private, or hybrid. In this article, we'll explain the difference between the three options, as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
Working in the cloud
To understand the different environments, it's useful to know what working in the cloud means. You no longer work within your local IT infrastructure but through a server hosted by an external provider (via the internet). That's where you store your data and/or run your software or computer programs. Thanks to the cloud, you can work wherever and whenever you want, as long as you have a stable internet connection. Some companies switch completely, while others opt for a hybrid solution. The best solution for you depends on the size of your company, your budget, and the activities of your organization. Let's see what the different options are.
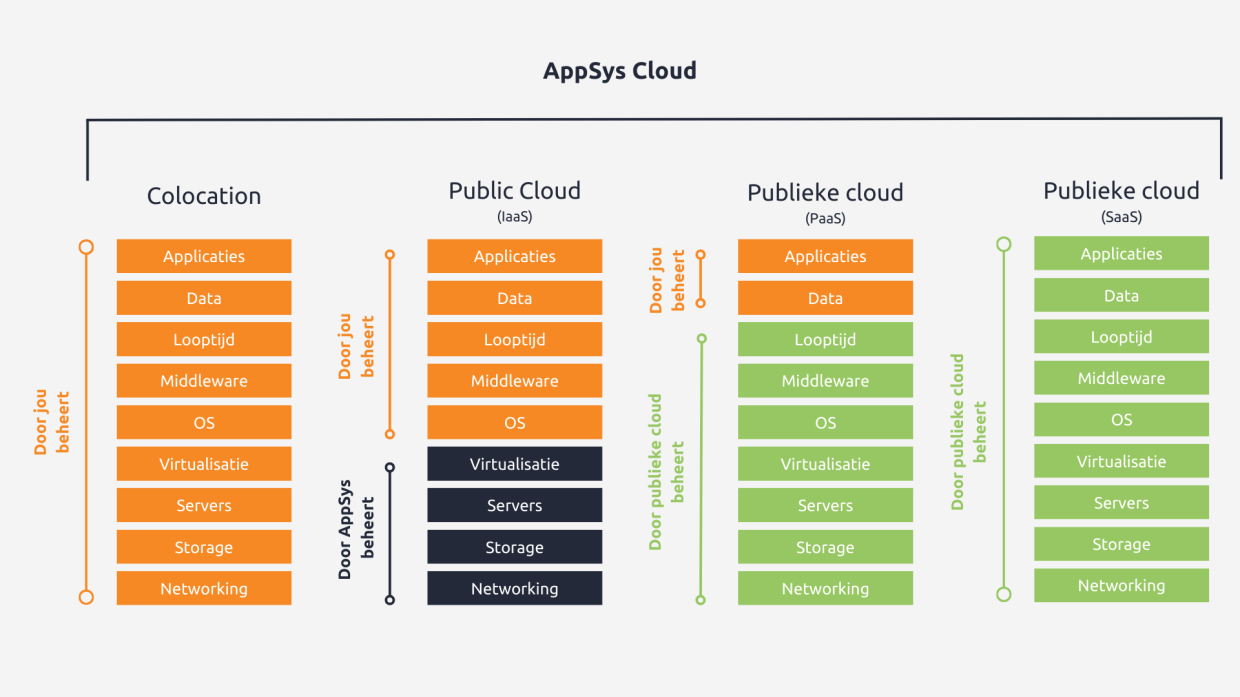
The Public Cloud
In a public cloud, you use a shared online infrastructure. You pay a certain amount per month or per year. The cloud environment is owned by a cloud provider and is used by multiple organizations. The most well-known public cloud environments are those of Microsoft, Google, and Amazon. At AppSys, in addition to our own cloud, we specialize in Microsoft Azure. Office365 is a recognizable example.
Advantages
- Flexibility: Public clouds are flexible and adapt to the changing needs of your organization.
- Scalability: It's easy to scale to meet the needs of your organization.
- Cost: Since you only consume services, you don't have to pay for hardware or its maintenance. These costs are often variable and are calculated based on your usage (data transfer, computing power, etc.).
Disadvantages
- Control: You have less control over the infrastructure and applications. This may not always align with certain mandates your organization must comply with (e.g., geographic location where your company data is stored).
- Standardization: Public clouds often offer standardized services and solutions. Although these can cover many of your company's needs, deviations are not always possible or may sometimes cost more.
- Cost: Although it's cheaper in terms of hardware or maintenance costs, it's often still considerably more expensive than opting for a private cloud.
The Private Cloud
On the other hand, we have the private cloud. Here, you privately acquire a portion of the cloud environment. This is not shared with another organization. The infrastructure of a private cloud is often hosted in an external data center (this is called colocation), but it can also be hosted on-premises. The underlying hardware can be self-managed or owned, or it can be rented.
Advantages
- Control: You have complete control over the infrastructure and applications.
- Security: You can fully configure your private cloud to meet the specific security requirements of your organization. Here, you have the choice of which security measures to provide.
- Tailor-made: A private cloud can be fully designed to precisely match the needs of your company.
- Easy Integration: A private cloud can better integrate with your existing IT infrastructure because it can often be better tailored to what your company actually needs.
Disadvantages
- Costs: Setting up and managing a private cloud can be expensive, especially if the hardware is owned.
- Complexity: Managing a private cloud can be complex, but we can help you with that.
The Hybrid Cloud
When you use both a private and a public cloud, you end up with a hybrid cloud solution. This means, for example, that you store your data in a private cloud but use Office365 (hosted in the public cloud). This is what organizations most commonly do.
Advantages
- The best of both worlds: A hybrid cloud offers the flexibility and scalability of a public cloud and the control and security of a private cloud.
- Cost-effectiveness: A hybrid cloud can be more cost-effective than just a private cloud or a public cloud.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Managing both environments can be complex, but we can help you with that.
And then there's our own AppSys Cloud
In theory, the AppSys Cloud is a public cloud. In practice, it works differently than the public clouds of Google or Amazon. It's a great alternative because it's much more budget-friendly. Additionally, you can choose whether to keep the servers in-house or partially or fully outsource them to us. Furthermore, you can expand the service with on- and off-site backup functionalities. Our AppSys Cloud is an accredited service provider for numerous software vendors. This allows us to offer many software licenses "as-a-Service."
Advantages
- Independent of physical machines
- High availability
- Maximum security
- VMware and Dell technology
- Quick installation, flexible, and scalable
- Secure backups
Finally: Colocation
In addition to choosing the cloud, there's another option for hosting your data elsewhere than in your own data center. With colocation, you place your own server in our data center. This means you don't have to invest in your own data center. From there, you can still decide whether to keep everything in-house, migrate your programs to the cloud, or keep them partially on-premises.
Visually, these different solutions look like this:
Would you like to learn more about your options in the cloud?
Contact us through this page.